Information
and Communication Technology (ICT)
- Information and Communication are two key words that represent global activity.
- Manager is surrounded by huge amount of data, but lacks the necessary information, which must be readily available to work in an effective way.
- The communication if the right information at the right time in a convenient form can cause new direction in Business Research and Industrial decisions.
- ICT consists of all technical means used to handle information and aid communication, including computer and network hardware, communication middleware as well as necessary software
Both data and information are types of knowledge or something used to attain knowledge. Though used interchangeably, there are many differences between the meanings of these two words.
- Data is a collection of raw facts and figures or a raw input which when processed or arranged makes meaningful output. (example student’s name, father name, mother name, address, etc.)
- Information is the data that is organized, meaningful and useful for making a decision. (example Total marks for each student, which are used to decide who is the topper.)
Data Processing
Data processing is the transformation of data into meaningful information.
| Data | Information |
| It is a collection of facts and figures. | It is a collection of final results. |
| It is in an unorganized (raw) form. | It is in an organized form. |
| It is not in directly useful form. | It is in directly useful form. |
| It needs processing. | It does not need any processing. |
| It is also termed as input. | It is also termed as output. |
| It requires observations and recordings. | It requires analysis. |
Information can be
Environment Information
Competitive Information
Internal Information
Information technology (IT)
IT is the use of computers to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data, or information, often in the context of a business or other enterprise. IT is considered to be a subset of information and communications technology (ICT).
75% of all information generated in the entire history of mankind has been generated in the last 30 years.Level of Information
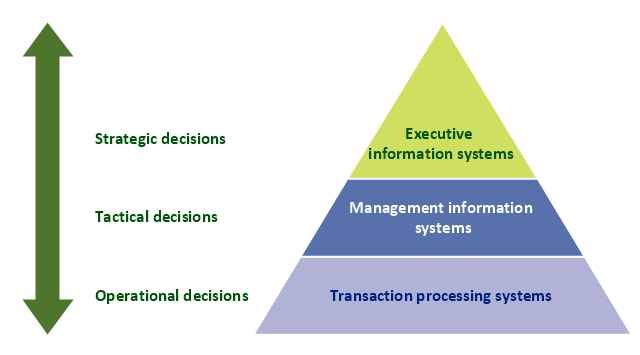
Information within an organisation can be analysed into 3 Levels.
- Strategic Information (Needed for long range planning and directions. This is less structured.)
- Tactical Information (Needed to take short range decisions to improve profitability and performance.)
- Operational Information (Needed for day to day operations of the organization. Ex: Daily Sales, Billing.)
- Accuracy
- Speed
- Paper Work can be Reduced
- Relevance
- Timeliness
- Completeness
- Purpose
- Reliability
- Validity
- Versatility
- Reduction in Manpower
Limitations of a Computer
- No Decision-making Ability
- No Intelligence
- No Emotions and Feelings
- Information is not consumed in use.
- It can be shared by many and can be used simultaneously without any loss to anyone.
- Scope – Detail /Summary, Complete set / specific exception, scope vary depend on level of management.
- No organisation has 100% exact information. Very often work with approximate information.
- Information may relate to History, near past, present, near future.
- Past information helps in forecasting the future.
- Hardware Cost
- System Analysis, Design and implementation Cost
- Cost of Space and Environment Control Factors
- Operations Cost

No comments:
Post a Comment